1. GENERAL INTRODUCTION TO THE PATENT LAW OF UNITED STATES
United States patent law is authorized by the U.S. Constitution, which is found under Title 35 of the United States Code. The U.S. Patent Law was approved on Jun.19th, 1952, which was amended in 1975, 1984 and 1999 respectively.
Article One, section 8, clause 8 states: the Congress shall have power ... To promote the progress of science and useful arts, by securing for limited times to authors and inventors the exclusive right to their respective writings and discoveries.
The United States is a member of Paris Convention and Patent Cooperation Treaty. Therefore, foreign enterprises and individuals can apply for a U.S. patent through the Paris Convention and the Patent Cooperation Treaty.
2. TYPE OF PATENT AND APPLICATION PROCESS
The type of US patent includes invention patent (Utility) and industrial design patent. According to the US Patent Law, USPTO carries out substantive examination to an invention patent application and industrial design patent. The duration of the invention patent right is 20 years, commencing from the date of application. The duration of the industrial design patent is 14 years, commencing from the date of registration.
2.1 Utility Patent
2.1.1 Concept and Description of the Invention Patent
In United States patent law, utility is a patentability requirement. As provided by 35 U.S.C. § 101, an invention is "useful" if it provides some identifiable benefit and is capable of use. The majority of inventions are usually not challenged as lacking utility, but the doctrine prevents the patenting of fantastic or hypothetical devices such as perpetual motion machines.
Under United States law, a patent is a right granted to the inventor of a process, machine, article of manufacture, or composition of matter, that is new, useful, and non-obvious. Section 102 of the patent act defines the "novelty" requirement. The novelty requirement prohibits patenting a technology that is already available to the public. To be patentable, a technology must not only be "new" but also "non-obvious." A technology is obvious (and therefore ineligible for a patent) if a person of "ordinary skill" in the relevant field of technology, as of the filing date of the patent application, would have thought the technology was obvious. Put differently, an invention that would have been obvious to a person of ordinary skill at the time of the invention is not patentable.
2.1.2 Application Process of an Invention Patent
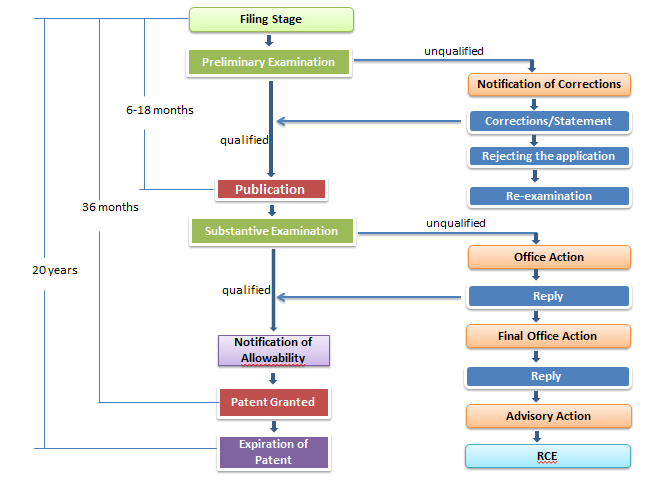
USPTO carries out substantive examination to the invention patent applications and industrial design patent applications, namely, examining the novelty, creativity of the invention patent applications.
2.1.3 Required Documents for Application
A. Application Form
B. Declaration
C. Written description, written claim, written abstract, drawings of written description and drawing of abstract.
D. Letter of authorization for the application of patent, which is required to be signed by the applicant or stamped (no notarization or certification is required).
E. Name and address of the applicant, name and address of the inventor, etc.
F. Assignment Letter
G. Priority document (if any)
H. Small Entity Declaration
Notes: all of the documents must be submitted in English.
2.2 Design Patent
2.2.1 Concept and Description of the Design Patent
According to the Patent Act of United States, “Industrial design” is a process of design applied to products that are to be manufactured through techniques of mass production. A design patent is a form of legal protection granted to the ornamental design of a functional item. Design patents are a type of industrial design right.
2.2.2 Application Process of a Design Patent
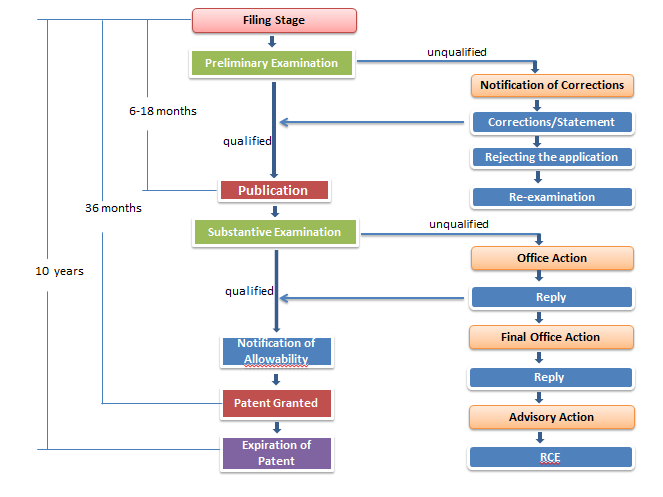
United States carries out substantive examination to an industrial design patent.
2.3.3 Required Documents for Application
A. Six-side views and three-dimensioned drawing;
B. Brief description of design patent, including name of product, application and design features, etc.
C. Letter of authorization for the application of patent, which is required to be signed by the applicant or stamped (no notarization or certification is required).
D. Name and address of the applicant, name and address of the inventor, etc.
Notes: all of the documents must be submitted in English.
3. PATENTABLE SUBJECT MATTER
"Whoever invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine, manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvement thereof may obtain a patent therefor, subject to the conditions and requirements of this title." 35 U.S.C. 101. To be patent eligible subject matter, an invention must meet two criteria. First, it must fall within one of the four statutory categories of acceptable subject matter: process, machine, manufacture, or composition of matter. Second, it must not be directed to subject matter encompassing a judicially recognized exception: laws of nature, physical phenomena, and abstract ideas.