1. GENERAL INTRODUCTION TO THE PATENT LAW IN MALAYSIA
The Patents Act (known as the Patents Act 1983) came into force in Malaysia on 1 October 1986, which was amended in 1993, 2000, 2002, 2003 and 2006.
Malaysia became a member of the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property on 1 January 1989.
Malaysia is also a contracting state to the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) and PCT applications may be filed in Malaysia from 16 August 2006 onwards.
Therefore, foreign enterprises and individuals can apply for a patent in Malaysia through the Paris Convention or enter national phase in Malaysia for a PCT application within a period of 30 months.
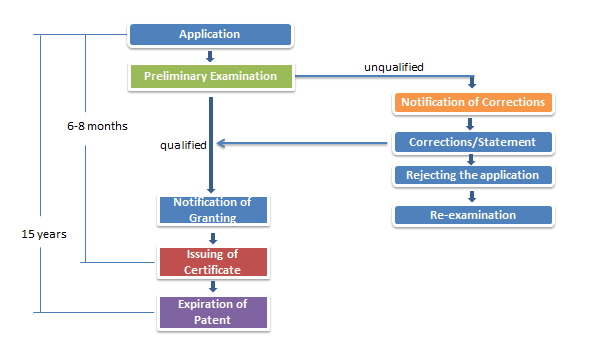
2. APPLICATION PROCESS OF A PATENT
According to the Patents Act 1983, the Patent Registration Office (MyIPO) will carry out substantive examination to an invention patent application. Applicants can opt for a request for Substantive Examination or Modified Substantive Examination. The duration of the patent is 20 years, commencing from the date of the application subject to the payment of annual renewal fees after grant.
2.1 Invention Patent
2.1.1 Concept and Description of the Invention Patent
According to Section 12 (1) of the Patent Acts 1983, the term “invention” refers to an idea of an inventor which permits in practice the solution to a specific problem in the field of technology.
An invention may be or may relate to a product or process.
“Product” refers to any thing which appears in tangible form, and includes any apparatus, article, device, equipment, handicraft, implement, machine, substance and composition. “Process” includes an art or a method.
It is required that the invention is new, involves an inventive step and is industrially applicable.
2.1.2 Application Process of an Invention Patent
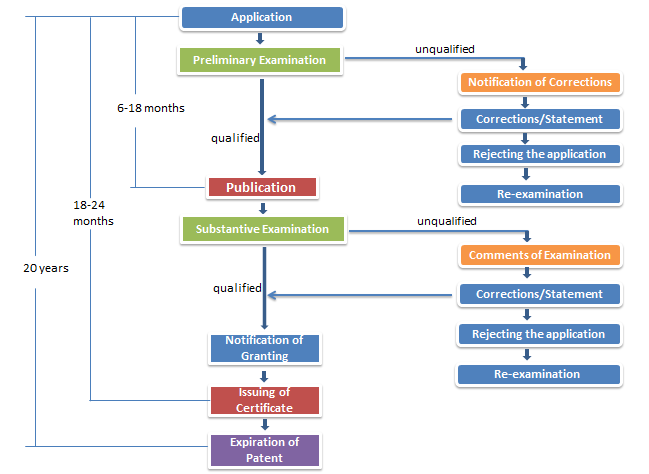
Malaysia carries out substantive examination on a patent application, namely, examining the novelty, inventiveness and industrial applicability of the invention.
2.1.3 Required Documents/ Information for Application
· Description of the invention.
· Claims.
· Drawings (if any).
· Abstract (if there are drawings, to be accompanied by the most illustrative of the drawings).
· A duly signed Appointment of Patent Agent (Patents Form No.17) with the name and designation of the signatory typed underneath the signature.
· If the applicant is not the inventor, a statement (Patents Form No. 22) on how the right to the invention was acquired.
· Name(s), address(es) and nationality(ies) of the Applicant(s).
· Name(s) and address(es) of the inventor(s).
· Priority details and/or PCT details.
2.2 Utility Innovation
2.2.1 Concept and Description of the Utility Innovation
According to Section 17 of the Patents Act 1983, the term “utility innovation” refers to any innovation which creates a new product or process, or any new improvement of a known product or process, which is capable of industrial application, and includes an invention. To obtain a certificate, an innovation need only be new, i.e. if there is any difference between the claim and what is already known, then the claim is new. Industrial applicability is also a requirement. Only one claim is allowed when filing a utility innovation.
2.2.2 Application Process of a Utility Innovation
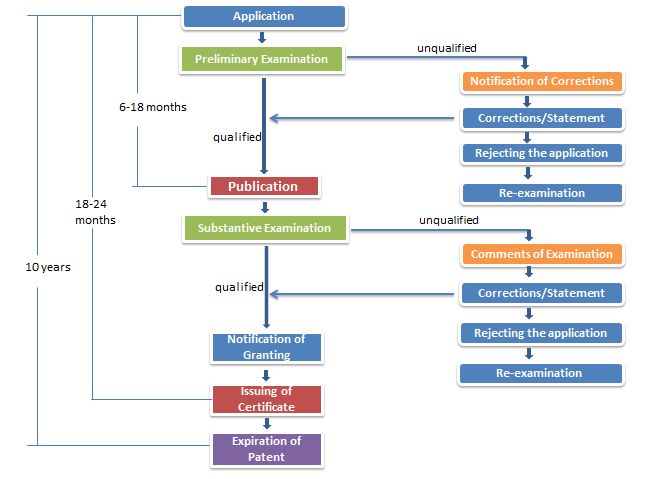
Similar to a patent application, the Patent Registration Office (MyIPO) will carry out substantive examination to a utility innovation application. Applicants can opt for a request for Substantive Examination or Modified Substantive Examination. A utility innovation application has a duration of 10 years, commencing from the date of application but may be extendible for two periods of 5 years each.
2.2.3 Required Documents/ Information for Application
· Description of the innovation.
· Claims (only 1 claim for a utility innovation).
· Drawings (if any).
· Abstract (if there are drawings, to be accompanied by the most illustrative of the drawings).
· A duly signed Appointment of Patent Agent (Patents Form No.17) with the name and designation of the signatory typed underneath the signature.
· If the applicant is not the innovator, a statement (Patents Form No. 22) on how the right to the invention was acquired.
· Name(s), address(es) and nationality(ies) of the Applicant(s).
· Name(s) and address(es) of the inventor(s).
· Priority details and/or PCT details.
2.3 Design Patent (Industrial Design)
2.3.1 Concept and Description of the Design Patent
Industrial designs in Malaysia are governed by the Industrial Designs Act 1996. An industrial design is the aesthetic feature of an article i.e. features of shape, configuration, pattern or ornament, which are applied to an article by any industrial process or means and has eye appeal.
2.3.2 Criteria for Registration
An industrial design is registrable if it has an eye appeal and is new. The industrial design is not considered to be new if prior to the application date of the application:
· the design has been publicly disclosed anywhere in the world; or
· the design was the subject matter of another application for registration of an industrial design filed in Malaysia by a different applicant having an earlier priority date.
2.3.3 Application Process of an Industrial Design
An application for registration of an industrial design must be made in the prescribed form and must be filed at the Industrial Design Registration Office (“IDRO”) together with the prescribed number of representations of the design (drawings/photographs), statement of novelty in respect of the industrial design and the prescribed filing fee. Once the documentation and the filing fee are properly filed, the IDRO will grant the official filing date of the application, which will be important in the event there are any issues of priority or time limits.
2.3.4 Examination
Thereafter, the Registrar shall conduct an examination of the design application to determine whether it complies with the formal requirements. If the Registrar is of the view that the application does not meet the formal requirements, the Registrar shall notify the applicant or the applicant’s agent to give him an opportunity to reply and/or to make the necessary amendments within a specified period so as to comply with those requirements.
2.3.5 Registration
Once the Registrar is satisfied that the application complies with the requisite formal requirements, the Registrar will proceed to have the design registered by recording the particulars in the Register and issue to the applicant a certificate of registration of the industrial design in the prescribed form. The certificate of registration shall be prima facie evidence of the facts and validity of the registration of the design.
The Registrar shall also cause the registered design to be published in the Official Journal by way of a notice that the industrial design has been registered together with the name and address of the registered owner as well as any other matters relating to the industrial design.
3.2.6 Required Information / Documents for Application
· Type of application:- single, multiple or whether the design is associated to any earlier design registration.
· Full name and address of the applicant; if the applicant is a corporation, then details of the kind of incorporation such as the country and state of incorporation is needed.
· If the applicant is not the author (artist), then the full name and address of the author is to be provided. The applicant must state how it acquired the right from the author, e.g. by virtue of a contract of employment, assignment, commission of work, etc.
· Name the article or set of articles to which the industrial design applies.
· International classification (class and sub-class) of the industrial design.
· Priority data: country, date, application number, international classification. If the applicant for priority is different from the proposed local application, the name of the original applicant must be provided and information as to how the right to priority was obtained should be specified, e.g. by virtue of an assignment executed on which date. A certified copy of the priority document must be filed in due course with the authorities along with a certified English translation of the priority document.
· Representations (drawings/photographs) of the article in all the different views bearing the industrial design to be on A-4 size paper (29.7cm x 21cm) and only one side to be used.
· The paper having the representation must have a left hand margin about 3 cm and the drawings/photographs must be in a size of not more than 12.5cm x 9cm (3R size photograph).
· A statement indicating where the novelty in the industrial design resides (such as in the shape, configuration, pattern or ornament applied to the article). This Statement of Novelty should be typed on the front of the first sheet of the representation.
· All documents filed must be in English or our national language.
· Designs Form 10 (Appointment of Agent) signed by the applicant.
3. WHAT SHALL NOT BE GRANTED
According to Section 13 of Patents Act 1983, for any of the following, no patent right shall be granted:
· discoveries, scientific theories and mathematical methods;
· plant or animal varieties or essentially biological processes for the production of plants or animals, other than man-made living micro-organisms, micro-biological processes and the products of such micro-organism processes;
· schemes, rules or methods for doing business, performing purely mental acts or playing games;
· methods for the treatment of human or animal body by surgery or therapy, and diagnostic methods practiced on the human or animal body:
Provided that this paragraph shall not apply to products used in any such methods:
An industrial design is not registrable if:
· it is a method or principle of construction; or
· the features are solely dictated by the function which the article has to perform; or
· the features are dependent upon the appearance of another article of which the article is intended by the author of the design to form an integral part.