1. GENERAL INTRODUCTION TO THE PATENT LAW OF INDONESIA
Indonesian patents are governed by the Patent Law, which was issued in 2001 and has undergone a number of amendments since its inception. The Indonesian Patent Law aims to provide for the registration and granting of patents for inventions and for matters connected therewith.
Indonesia acceded to the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property and became a signatory of the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT). Indonesia has been a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO) since 1 January 1995. Therefore, foreign enterprises and individuals can apply for an Indonesian patent through the Paris Convention and the Patent Cooperation Treaty.
2. TYPE OF PATENT AND APPLICATION PROCESS
The type of Indonesian patent comprises invention, simple patent and design. According to the Indonesian Patent Law, the patent administration department (DGIP) may carry out a substantive examination to an invention patent application, and a preliminary examination to a simple patent application. The duration of the invention patent right is 20 years, commencing from the date of application. The duration of a simple patent is 10 years and the duration of a design patent is 10 years, commencing from the date of application. DGIP carries out a preliminary examination to a design patent application. It is important to note that, at present, DGIP may appropriately examine the novelty of an invention patent application.
2.1 Invention Patent
2.1.1 Concept and Description of the Invention Patent
According to the Indonesian Patent Law, the term “invention” refers to any new technical solution relating to a product, a process or an improvement thereof.
“Product” refers to all kinds of new products manufactured by industrial methods, including items with a certain shape and structure, such as solid, liquid and gas. “Method” refers to the method of processing the raw materials into a variety of products. It is not required that an invention patent can be directly applied to industrial production and technological achievements. It can be a solution or an idea to solve the technical problem, having the possibility of industrial application. However, such technical solution or idea should not be confused with proposing pure conceptions because pure conceptions cannot be applied to industrial applications.
2.1.2 Application Process of an Invention Patent
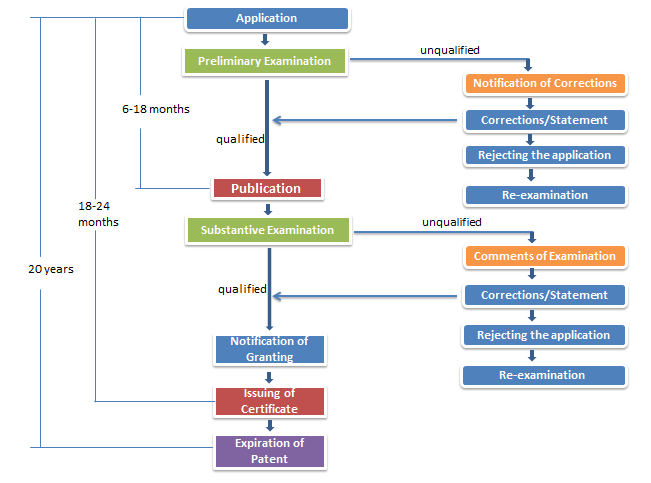
Similar to most of the countries, Indonesia carries out substantive examination to the invention patent applications, namely, examining the novelty, creativity of the invention patent applications.
2.1.3 Required Documents for Application
A. Written description, written claim, written abstract, drawings of written description and drawing of abstract.
B. Letter of authorization for the application of patent, which is required to be signed by the applicant or stamped (no notarization or certification is required).
C. Name and address of the applicant, name and address of the inventor, etc.
Notes: all of the documents must be submitted in Indonesian.
2.2 Simple Patent
2.2.1 Concept and Description of the Simple Patent
According to the Indonesian Patent Law, the term “simple patent” refers to any new technical solution relating to a product’s shape, structure, or a combination thereof, which is fit for practical use. Same as an invention patent, a simple patent also protects a technical solution. However, the protective scope of the simple patent is comparatively smaller, namely, merely protecting the new products with a certain shape or structure. A simple patent DOES NOT protect the method and the substance without a definite shape. Comparing with the invention patent, simple patent pays special attention to the industrial practicability of the technical solution, and the technical level of a simple patent is lower than that of an invention patent. The simple patent in most of the countries protects those simpler and modified technical inventions, which can also be called “small inventions”.
2.2.2 Application Process of a Simple Patent
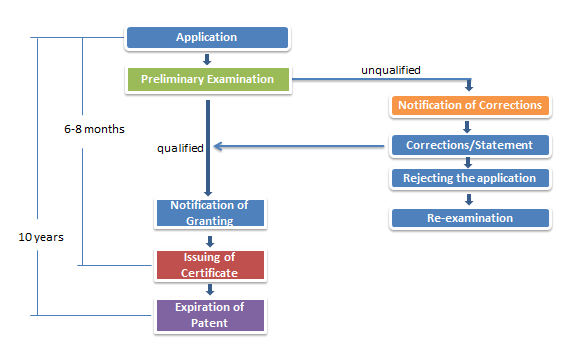
Similar to most of the countries, DGIP carries out preliminary examination to the simple patent t application.
2.2.3 Required Documents for Application
A. Written description, written claim, written abstract, drawings of written description and drawing of abstract.
B. Letter of authorization for the application of patent, which is required to be signed by the applicant or stamped (no notarization or certification is required).
C. Name and address of the applicant, name and address of the inventor, etc.
Notes: all of the documents must be submitted in Indonesian.
2.3 Design Patent
2.3.1 Concept and Description of the Design Patent
According to the Indonesian Patent Law, the term “design” refers to any new design of a product’s shape, pattern or a combination thereof, as well as the combination of the color and the shape or pattern of a product, which creates an aesthetic feeling and is fit for industrial application. It is also stipulated in the Indonesian Patent Law that any design for which a patent is granted shall not be attributed to the existing design, and no entity or individual has, before the date of application, filed an application with the patent administrative department (DGIP) on the identical design and recorded it in the patent documents published after the date of application.
2.3.2 Application Process of a Design Patent
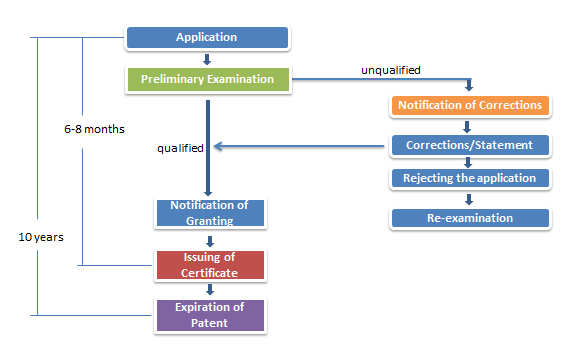
Similar to most of the countries, DGIP carries out preliminary examination to a design patent application instead of substantive examination.
2.3.3 Required Documents for Application
A. Six-side views and three-dimensioned drawing;
B. Brief description of design patent, including name of product, application and design features, etc.
C. Letter of authorization for the application of patent, which is required to be signed by the applicant or stamped (no notarization or certification is required).
D. Name and address of the applicant, name and address of the inventor, etc.
Notes: all of the documents must be submitted in Indonesian.
3. WHAT SHALL NOT BE GRANTED
According to the Indonesian Patent Law, for any of the following, no patent right shall be granted:
(1) Scientific discoveries;
(2) Rules and methods for mental activities;
(3) Methods for the diagnosis or for the treatment of diseases;
(4) Animal and plant varieties;
(5) Substances obtained by means of nuclear transformation; and
(6) The design, which is used primarily for the identification of pattern, color or the combination of the two on printed flat works.